Assembly Services
The Service Factory provides different services depending on the need. The purpose of the Service factory is to separate code by type of function which allows for more flexibility and easier maintenance.
Configuration
The service factory can be used by creating a file of type ServiceFactory in your assembly. Once created, this rule will contain commented out code that can be used to call different services.
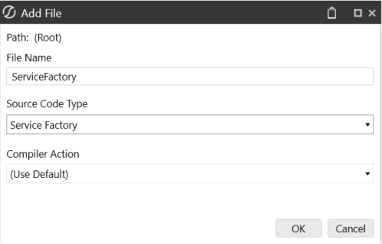
The object will invoke different Services depending on the task. Ensure you enable your desired service by uncommenting / enabling the code for that service in your service factory file. In this example the dashboard service has been enabled.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Data;
using System.Data.Common;
using System.Globalization;
using System.IO;
using System.Linq;
using Microsoft.CSharp;
using OneStream.Finance.Database;
using OneStream.Finance.Engine;
using OneStream.Shared.Common;
using OneStream.Shared.Database;
using OneStream.Shared.Engine;
using OneStream.Shared.Wcf;
using OneStream.Stage.Database;
using OneStream.Stage.Engine;
using OneStreamWorkspacesApi;
using OneStreamWorkspacesApi.V800;
namespace Workspace.__WsNamespacePrefix.__WsAssemblyName
{
public class wsServiceFactory : IWsAssemblyServiceFactory
{
public IWsAssemblyServiceBase CreateWsAssemblyServiceInstance(SessionInfo si, BRGlobals brGlobals,
DashboardWorkspace workspace, WsAssemblyServiceType wsAssemblyServiceType, string itemName)
{
try
{
switch (wsAssemblyServiceType)
{
//case WsAssemblyServiceType.Component:
// return new WsasComponent();
//case WsAssemblyServiceType.Dashboard:
// return new WsasDashboard();
//case WsAssemblyServiceType.DataManagementStep:
// return new WsasDataManagementStep();
//case WsAssemblyServiceType.DataSet:
// return new WsasDataSet();
//case WsAssemblyServiceType.DynamicDashboards:
// return new WsasDynamicDashboards();
//case WsAssemblyServiceType.FinanceCore:
// return new WsasFinanceCore();
//case WsAssemblyServiceType.FinanceCustomCalculate:
// return new WsasFinanceCustomCalculate();
//case WsAssemblyServiceType.FinanceGetDataCell:
// return new WsasFinanceGetDataCell();
//case WsAssemblyServiceType.FinanceMemberLists:
// return new WsasFinanceMemberLists();
//case WsAssemblyServiceType.SqlTableEditor:
// return new WsasSqlTableEditor();
//case WsAssemblyServiceType.TableView:
// return new WsasTableView();
//case WsAssemblyServiceType.XFBRString:
// return new WsasXFBRString();
default:
return null;
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
throw new XFException(si, ex);
}
}
}
}
Once enabled you can create a file with the same name as the desired service, in this case, a DashboardService file named WsasDashboard.
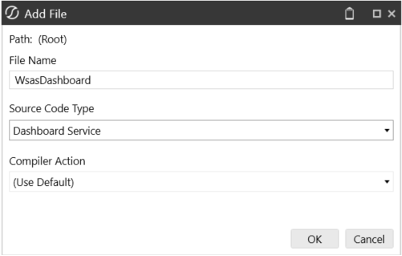
This file can be named differently if needed, as long as the naming is also changed in the Service Factory File.
After creating the necessary files, the Workspace Assembly Service must be specified at either the Workspace or Maintenance Unit level, depending on where the service factory will be used. This can be done by specifying AssemblyName.ServiceFactoryName in the Workspace Assembly Service field.
Using Assembly Services
Once enabled, you can call the service from your component, dashboard, data management job, etc. with a simple call in the server task field. If enabled at the Workspace level the call can be made using the syntax {WS}{FunctionName}{Param=[Value]}.
If enabled at the Maintenance Unit Level, WS should be replaced with WSMU.
Available Service Types
There are a number of service types available in the Service Factory. Below are some common service types and their usage:
- Component Service Type
- Dashboard Service Type
- Data Set Service Type
- Dynamic Dashboard Service Type
- SQL Table Editor Service Type
- Table View Service Type
- XFBRString Service Type
Component Service Type
The Component Service type enables you to implement a ComponentSelectionChanged function within a dashboard extender rule defined in assemblies. You can create this function either by selecting the Component Service type or by choosing the Dashboard Extender business rule type. Dashboard extender rules are primarily used to execute custom tasks within workspaces and are designed to handle events triggered by user interactions with dashboard components, such as grids or combo boxes. These rules are referenced via the action properties of individual components.
Service Factory Setup
To begin, create a Service Factory. This file is used to interact with dynamic dashboards and supports the creation of OneStream objects.
-
Create a new Workspace, Name:
Dynamic Dashboard Examples -
Add a Maintenance Unit, Type:
CodeOnly -
Add an Assembly, Type:
Code -
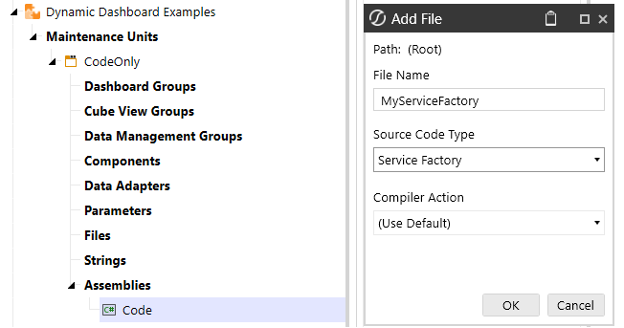
Add a New File to the Assembly:
- Navigate to the Code section under the Assembly Files panel. Right-click on Files and select Add File.
- Set Source Code Type to
Service Factory.
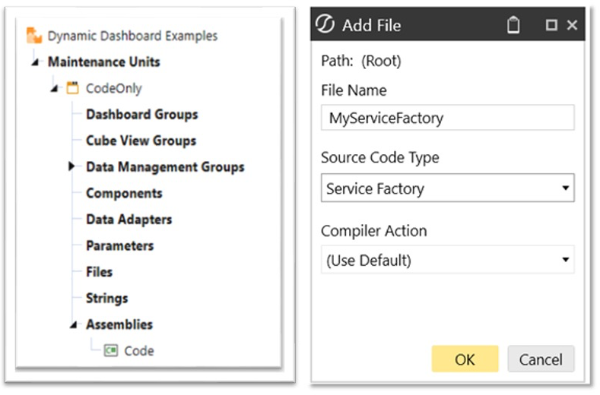
-
Review the provided source code for
MyServiceFactoryand ensure that the Component case statement is uncommented. -
Rename the returning class as needed. (Optional)
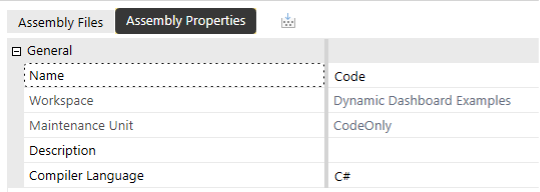
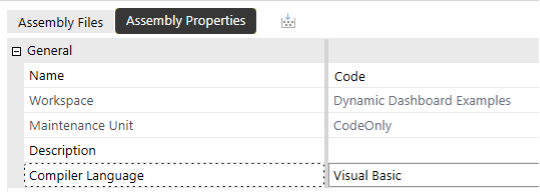
- C#
- Visual Basic
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Data;
using System.Data.Common;
using System.Globalization;
using System.IO;
using System.Linq;
using Microsoft.CSharp;
using OneStream.Finance.Database;
using OneStream.Finance.Engine;
using OneStream.Shared.Common;
using OneStream.Shared.Database;
using OneStream.Shared.Engine;
using OneStream.Shared.Wcf;
using OneStream.Stage.Database;
using OneStream.Stage.Engine;
using OneStreamWorkspacesApi;
using OneStreamWorkspacesApi.V800;
namespace Workspace.__WsNamespacePrefix.__WsAssemblyName
{
public class MyServiceFactory : IWsAssemblyServiceFactory
{
public IWsAssemblyServiceBase CreateWsAssemblyServiceInstance (SessionInfo si, BRGlobals brGlobals,
DashboardWorkspace workspace, WsAssemblyServiceType wsAssemblyServiceType, string itemName)
{
try
{
switch (wsAssemblyServiceType)
{
case WsAssemblyServiceType.Component:
return new WsasComponent();
//case WsAssemblyServiceType.Dashboard:
// return new WsasDashboard();
//case WsAssemblyServiceType.DataManagementStep:
// return new WsasDataManagementStep();
//case WsAssemblyServiceType.DataSet:
// return new WsasDataSet();
//case WsAssemblyServiceType.DynamicDashboards:
// return new WsasDynamicDashboards();
//case WsAssemblyServiceType.FinanceCore:
// return new WsasFinanceCore();
//case WsAssemblyServiceType.FinanceCustomCalculate:
// return new WsasFinanceCustomCalculate();
//case WsAssemblyServiceType.FinanceGetDataCell:
// return new WsasFinanceGetDataCell();
//case WsAssemblyServiceType.FinanceMemberLists:
// return new WsasFinanceMemberLists();
//case WsAssemblyServiceType.SqlTableEditor:
// return new WsasSqlTableEditor();
//case WsAssemblyServiceType.TableView:
// return new WsasTableView();
//case WsAssemblyServiceType.XFBRString:
// return new WsasXFBRString();
default:
return null;
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
throw new XFException(si, ex);
}
}
}
}
Imports System
Imports System.Collections.Generic
Imports System.Data
Imports System.Data.Common
Imports System.Globalization
Imports System.IO
Imports System.Linq
Imports Microsoft.CSharp
Imports OneStream.Finance.Database
Imports OneStream.Finance.Engine
Imports OneStream.[Shared].Common
Imports OneStream.[Shared].Database
Imports OneStream.[Shared].Engine
Imports OneStream.[Shared].Wcf
Imports OneStream.Stage.Database
Imports OneStream.Stage.Engine
Imports OneStreamWorkspacesApi
Imports OneStreamWorkspacesApi.V800
Namespace Workspace.__WsNamespacePrefix.__WsAssemblyName
Public Class MyServiceFactory
Inherits IWsAssemblyServiceFactory
Public Function CreateWsAssemblyServiceInstance(ByVal si As SessionInfo, ByVal brGlobals As BRGlobals, ByVal workspace As DashboardWorkspace, ByVal wsAssemblyServiceType As WsAssemblyServiceType, ByVal itemName As String) As IWsAssemblyServiceBase
Try
Select Case wsAssemblyServiceType
Case WsAssemblyServiceType.Component
Return New WsasComponent()
'Case WsAssemblyServiceType.Dashboard
' Return New WsasDashboard()
'Case WsAssemblyServiceType.DataManagementStep
' Return New WsasDataManagementStep()
'Case WsAssemblyServiceType.DataSet
' Return New WsasDataSet()
'Case WsAssemblyServiceType.DynamicDashboards
' Return New WsasDynamicDashboards()
'Case WsAssemblyServiceType.FinanceCore
' Return New WsasFinanceCore()
'Case WsAssemblyServiceType.FinanceCustomCalculate
' Return New WsasFinanceCustomCalculate()
'Case WsAssemblyServiceType.FinanceGetDataCell
' Return New WsasFinanceGetDataCell()
'Case WsAssemblyServiceType.FinanceMemberLists
' Return New WsasFinanceMemberLists()
'Case WsAssemblyServiceType.SqlTableEditor
' Return New WsasSqlTableEditor()
'Case WsAssemblyServiceType.TableView
' Return New WsasTableView()
'Case WsAssemblyServiceType.XFBRString
' Return New WsasXFBRString()
Case Else
Return Nothing
End Select
Catch ex As Exception
Throw New XFException(si, ex)
End Try
End Function
End Class
End Namespace
Select the workspace and update the Workspace Assembly Service property value to the format {WsAssemblyName}.{ServiceFactoryName}. For example, set the value to Code.MyServiceFactory.
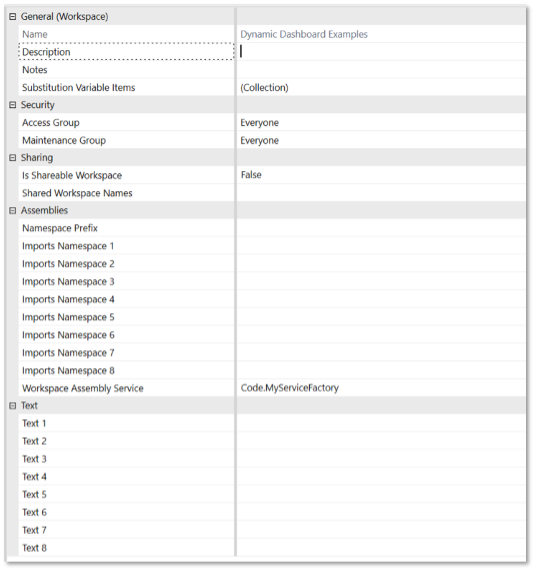
Component Service
After you have created the Service Factory file and uncommented the required lines of code, proceed with the creation of a Component Service:
-
Add a New File:
- Navigate to the Code section.
- In the Assembly Files panel, right-click on Files and select Add File.
- Set the File Name to match the returning class name.
- Set Source Code Type to Component Service.

Example – Dynamic Dashboard Sample
This example uses the Dynamic Dashboards sample located under Components -> Dynamic Dashboards. The following steps add code to display a message box when a user clicks a button. Ensure that the Dynamic Dashboards case statement in the MyServiceFactory code is uncommented.
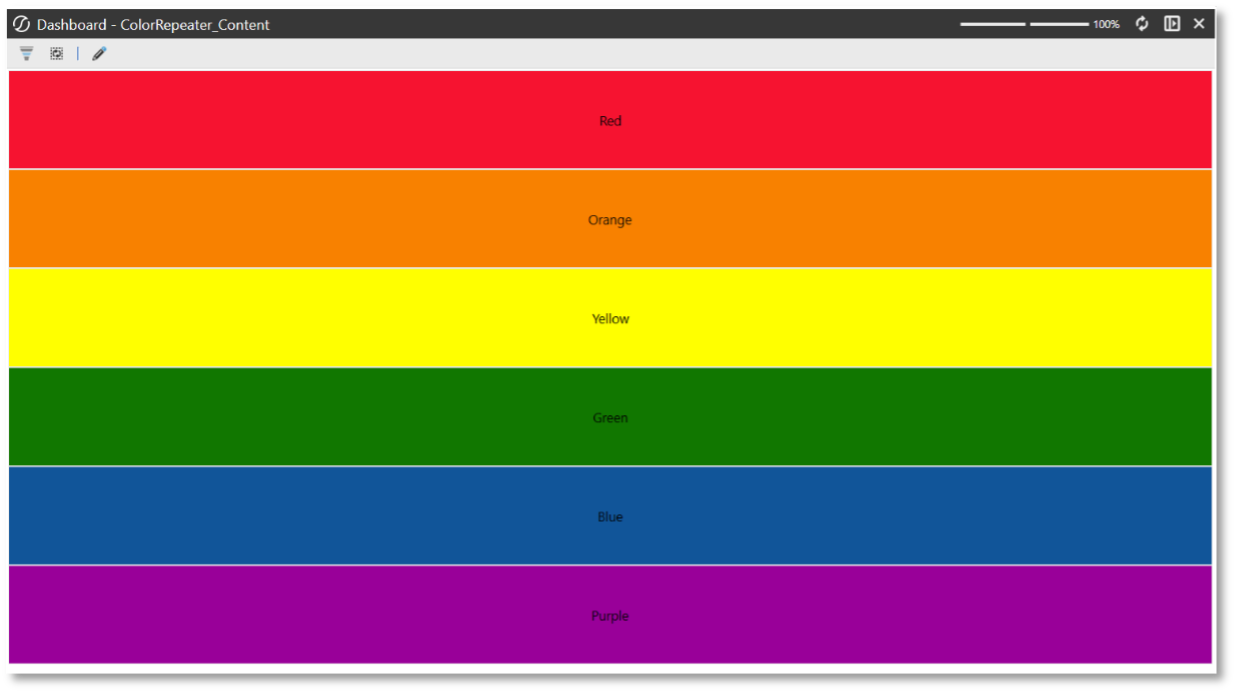
-
Navigate to Workspaces -> Dynamic Dashboard Examples -> Maintenance Units -> CodeOnly -> Components -> Button.
-
Click on the button (
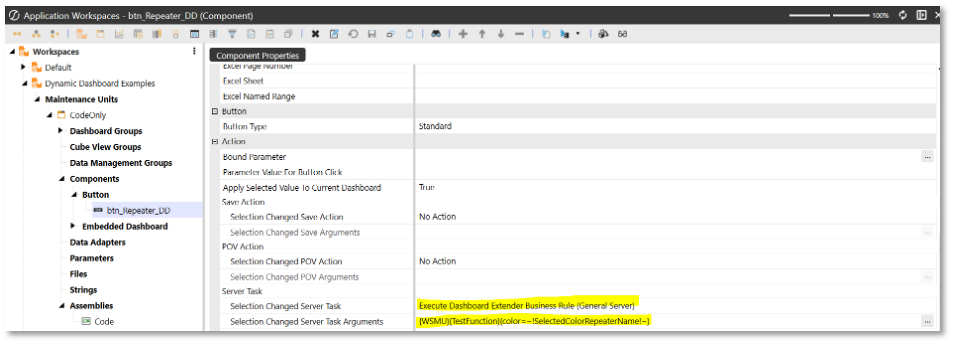
btn_Repeater_DD) created in the dynamic dashboard sample. -
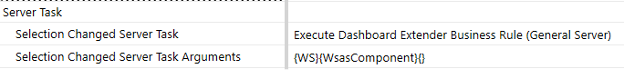
Update the value of Selection Changed Server Task to
Execute Dashboard Extender Business Rule (General Server). -
Update the value of Selection Changed Server Task Arguments to the following:
{WSMU}{TestFunction}{color=~!SelectedColorRepeaterName!~}The screenshot below is for reference.
The syntax for referencing an object at the global level is {WS}{FunctionName}{Parameter1=Value1}.
The syntax for using the Assembly Service at the Maintenance level is {WSMU}{FunctionName}{Parameter1=Value1}.
- Click Save after updating the properties.
- Open the newly created Components assembly file and add the highlighted code lines as indicated in the sample.
- C#
- Visual Basic
namespace Workspace.__WsNamespacePrefix.__WsAssemblyName
{
public class WsasComponent : IWsasComponentV800
{
public XFSelectionChangedTaskResult ProcessComponentSelectionChanged(SessionInfo si, BRGlobals brGlobals, DashboardWorkspace workspace, WsAssemblyServiceType wsAssemblyServiceType, string itemName)
{
try
{
if ((brGlobals != null) && (workspace != null) && (args?.SelectionChangedTaskInfo != null))
{
if (args.FunctionName.XFEqualsIgnoreCase("TestFunction"))
{
//Implement Dashboard Component Selection Changed Logic here.
var selectionChangedTaskResult = new XFSelectionChangedTaskResult();
selectionChangedTaskResult.IsOK = true;
string color = args.NameValuePairs.XFGetValue("color");
selectionChangedTaskResult.ShowMessageBox = true;
selectionChangedTaskResult.Message = $"You clicked on {color}";
selectionChangedTaskResult.ChangeSelectionChangedUIActionInDashboard = false;
selectionChangedTaskResult.ModifiedSelectionChangedUIActionInfo = null;
selectionChangedTaskResult.ChangeSelectionChangedNavigationInDashboard = false;
selectionChangedTaskResult.ModifiedSelectionChangedNavigationInfo = null;
selectionChangedTaskResult.ChangeCustomSubstVarsInDashboard = false;
selectionChangedTaskResult.ModifiedCustomSubstVars = null;
selectionChangedTaskResult.ChangeCustomSubstVarsInLaunchedDashboard = false;
selectionChangedTaskResult.ModifiedCustomSubstVarsForLaunchedDashboard = null;
return selectionChangedTaskResult;
}
}
return null;
}
}
}
}
Namespace Workspace.__WsNamespacePrefix.__WsAssemblyName
Public Class WsasComponent
Inherits IWsasComponentV800
Public Function ProcessComponentSelectionChanged(ByVal si As SessionInfo, ByVal brGlobals As BRGlobals, ByVal workspace As DashboardWorkspace, ByVal wsAssemblyServiceType As WsAssemblyServiceType, ByVal itemName As String) As XFSelectionChangedTaskResult
Try
If (brGlobals IsNot Nothing) AndAlso (workspace IsNot Nothing) AndAlso (args?.SelectionChangedTaskInfo IsNot Nothing) Then
If args.FunctionName.XFEqualsIgnoreCase("TestFunction") Then
Dim selectionChangedTaskResult = New XFSelectionChangedTaskResult()
selectionChangedTaskResult.IsOK = True
Dim color As String = args.NameValuePairs.XFGetValue("color")
selectionChangedTaskResult.ShowMessageBox = True
selectionChangedTaskResult.Message = $"You clicked on {color}"
selectionChangedTaskResult.ChangeSelectionChangedUIActionInDashboard = False
selectionChangedTaskResult.ModifiedSelectionChangedUIActionInfo = Nothing
selectionChangedTaskResult.ChangeSelectionChangedNavigationInDashboard = False
selectionChangedTaskResult.ModifiedSelectionChangedNavigationInfo = Nothing
selectionChangedTaskResult.ChangeCustomSubstVarsInDashboard = False
selectionChangedTaskResult.ModifiedCustomSubstVars = Nothing
selectionChangedTaskResult.ChangeCustomSubstVarsInLaunchedDashboard = False
selectionChangedTaskResult.ModifiedCustomSubstVarsForLaunchedDashboard = Nothing
Return selectionChangedTaskResult
End If
End If
Return Nothing
Finally
End Try
End Function
End Class
End Namespace
- Click Save.
- Click View Dashboard to launch the Dynamic Repeater Dashboard in OneStream. When clicking on the buttons, a message box should display the color corresponding to the clicked button. A screenshot of the expected output is provided below.
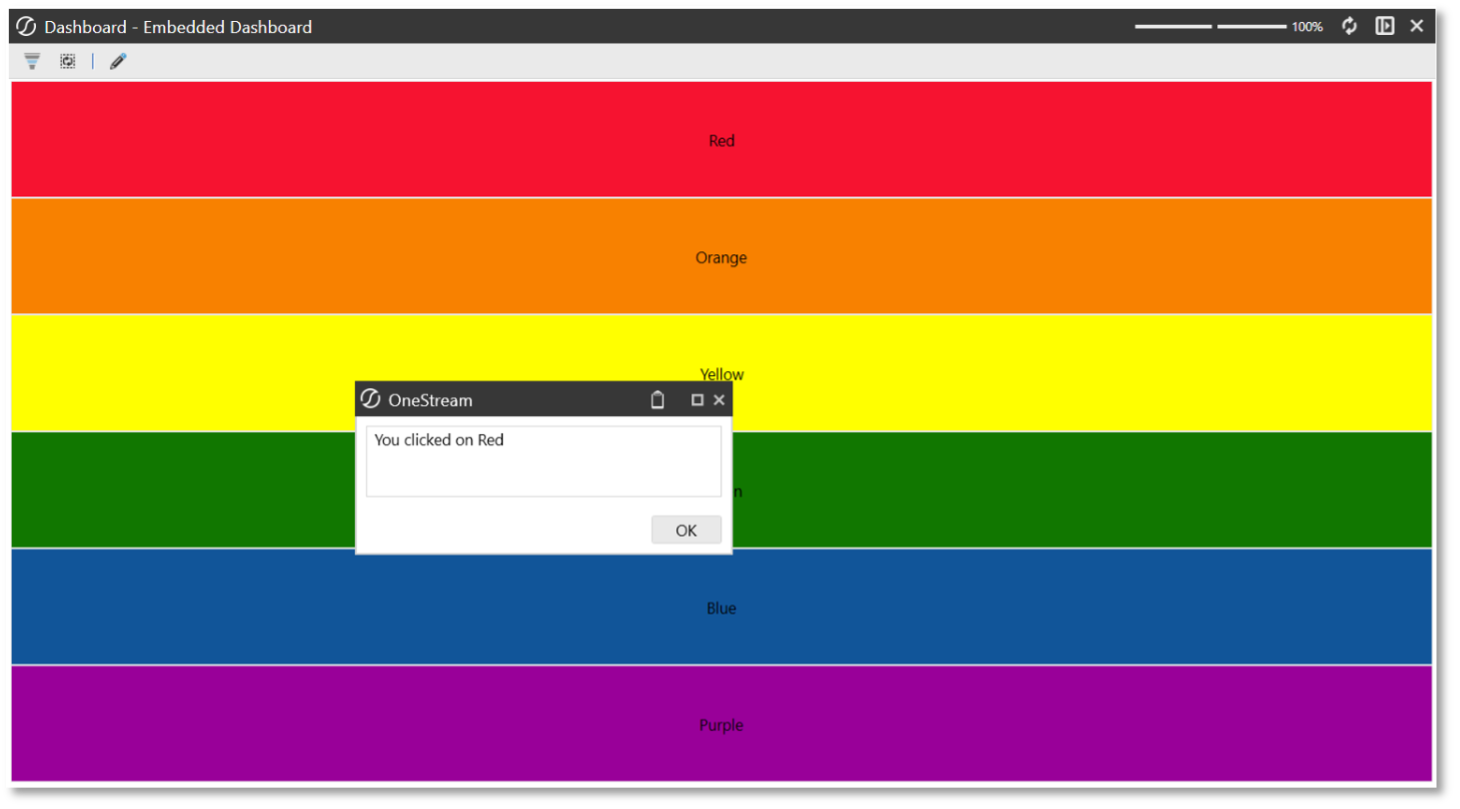
Dashboard Service Type
This service type lets you create a LoadDashboard function type in a dashboard extender rule within assemblies. You can do this by choosing this service type or by choosing the Dashboard Extender business rule type. These rules are usually used to perform custom tasks within workspaces. Developers often use the Dashboard service type with selection components, such as combo boxes to set parameters to a default value or the last selected value.
Service Factory Setup
Start by creating a Service Factory. The Service Factory file is used to interact with dynamic dashboards and allows for the creation of OneStream objects.
- Create a new Workspace (Dynamic Dashboard Examples)
- Add a Maintenance Unit (CodeOnly)
- Add an Assembly (Code) and choose the Compiler Language C# or Visual Basic. Throughout the remainder of this document, the C# image will precede the Visual Basic example.
- Click Save.
- Click on Code, and under the Assembly Files panel, right-click Files. Then click on Add File.
- Source Code Type =
Service Factory
- Source Code Type =
The source code for MyServiceFactory is below. Uncomment the Dashboard case statement for C# or Visual Basic, and rename the returning class (optional).
- C#
- Visual Basic
namespace Workspace.__WsNamespacePrefix.__WsAssemblyName
{
public class MyServiceFactory : IWsAssemblyServiceFactory
{
public IWsAssemblyServiceBase CreateWsAssemblyServiceInstance(SessionInfo si, BRGlobals brGlobals,
DashboardWorkspace workspace, WsAssemblyServiceType wsAssemblyServiceType, string itemName)
{
try
{
switch (wsAssemblyServiceType)
{
//case WsAssemblyServiceType.Component:
// return new WsasComponent();
case WsAssemblyServiceType.Dashboard:
return new WsasDashboard();
//case WsAssemblyServiceType.DataManagementStep:
// return new WsasDataManagementStep();
//case WsAssemblyServiceType.DataSet:
// return new WsasDataSet();
//case WsAssemblyServiceType.DynamicDashboards:
// return new WsasDynamicDashboards();
//case WsAssemblyServiceType.FinanceCore:
// return new WsasFinanceCore();
//case WsAssemblyServiceType.FinanceCustomCalculate:
// return new WsasFinanceCustomCalculate();
//case WsAssemblyServiceType.FinanceGetDataCell:
// return new WsasFinanceGetDataCell();
//case WsAssemblyServiceType.FinanceMemberLists:
// return new WsasFinanceMemberLists();
//case WsAssemblyServiceType.SqlTableEditor:
// return new WsasSqlTableEditor();
//case WsAssemblyServiceType.TableView:
// return new WsasTableView();
//case WsAssemblyServiceType.XFBRString:
// return new WsasXFBRString();
default:
return null;
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
throw new XFException(si, ex);
}
}
}
}
Namespace Workspace.__WsNamespacePrefix.__WsAssemblyName
Public Class MyServiceFactory
Implements IWsAssemblyServiceFactory
Public Function CreateWsAssemblyServiceInstance(ByVal si As SessionInfo, ByVal globals As BRGlobals, ByVal workspace As DashboardWorkspace, ByVal wsasType As WsAssemblyServiceType, ByVal itemName As String) As IWsAssemblyServiceBase Implements IWsAssemblyServiceFactory.CreateWsAssemblyServiceInstance
Try
Select Case wsasType
Case Is = WsAssemblyServiceType.Component
'Return New WsasComponent()
Case Is = WsAssemblyServiceType.Dashboard
Return New WsasDashboard()
Case Is = WsAssemblyServiceType.DataManagementStep
'Return New WsasDataManagementStep()
Case Is = WsAssemblyServiceType.DataSet
'Return New WsasDataSet()
Case Is = WsAssemblyServiceType.DynamicDashboards
'Return New WsasDynamicDashboards()
Case Is = WsAssemblyServiceType.FinanceCore
'Return New WsasFinanceCore()
Case Is = WsAssemblyServiceType.FinanceCustomCalculate
'Return New WsasFinanceCustomCalculate()
Case Is = WsAssemblyServiceType.FinanceGetDataCell
'Return New WsasFinanceGetDataCell()
Case Is = WsAssemblyServiceType.FinanceMemberLists
'Return New WsasFinanceMemberLists()
Case Is = WsAssemblyServiceType.SqlTableEditor
'Return New WsasSqlTableEditor()
Case Is = WsAssemblyServiceType.TableView
'Return New WsasTableView()
Case Is = WsAssemblyServiceType.XFBRString
'Return New WsasXFBRString()
Case Else
Return Nothing
End Select
Return Nothing
Catch ex As Exception
Throw New XFException(si, ex)
End Try
End Function
End Class
End Namespace
- Select the workspace and update the Workspace Assembly Service property to
{WsAssemblyName}.{ServiceFactoryName}. For example,Code.MyServiceFactory
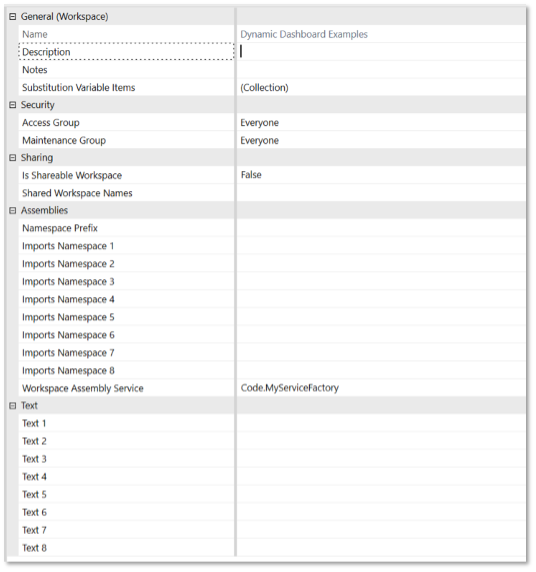
- Click Save.
Dashboard Service
Once the Service Factory file has been created and the appropriate lines of code have been uncommented, create a Dashboard Service.
- Click on Code, and under the Assembly Files panel, right-click Files. Then click on Add File.
- File Name =
Returning class name - Source Code Type = Dashboard Service
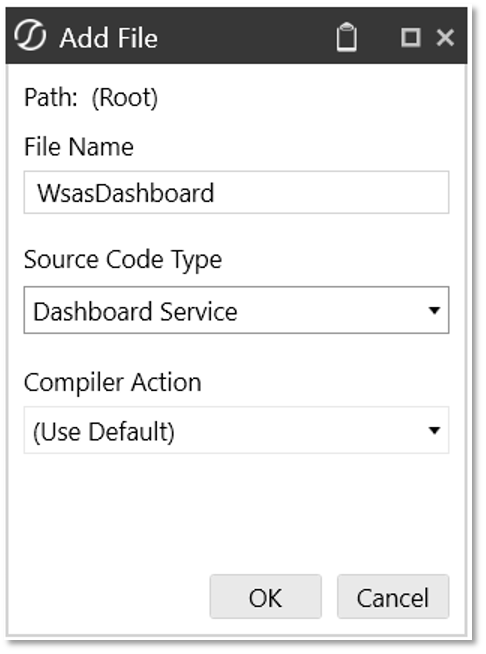
- Click OK.
Example
The following is from the Dynamic Dashboards sample that can be found under Dynamic Dashboards. We will be using code to add a header message instead of adding the message manually. For this to work properly, please make sure that the Dynamic Dashboards case statement from the MyServiceFactory code is uncommented out.

- Under Workspaces -> Dynamic Dashboard Examples -> Maintenance Units -> CodeOnly -> Dashboard Groups -> Repeater, click on the dashboard (
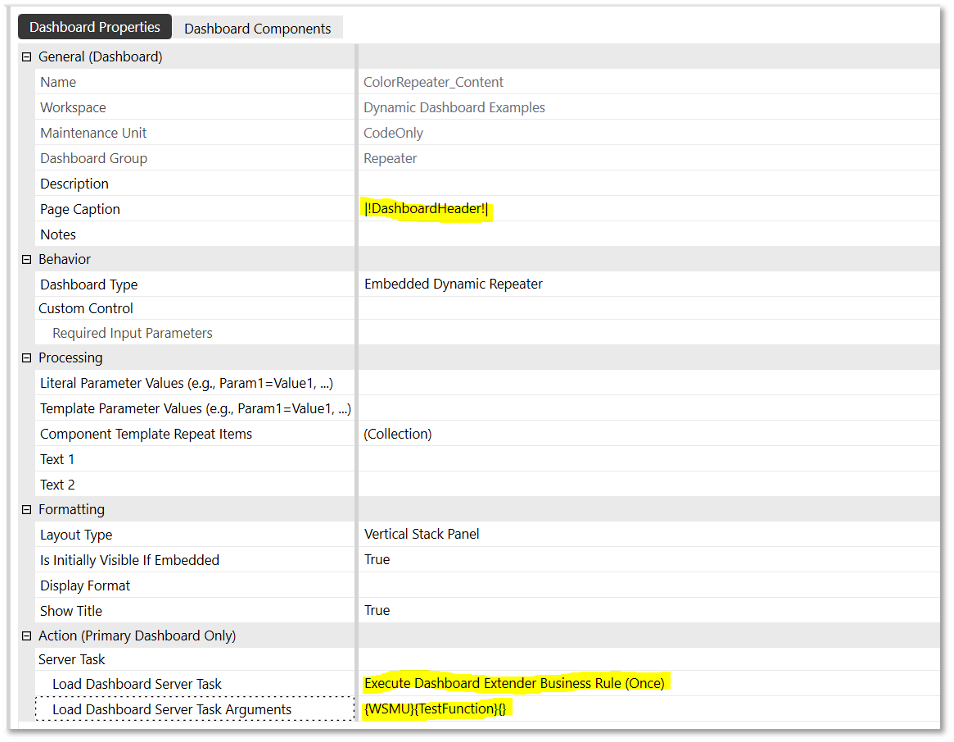
ColorRepeater_Content) that was previously created in the dynamic dashboard sample. - Update the value of Page Caption to
|!DashboardHeader!|. - Update the value of Load Dashboard Server Task to
Execute Dashboard Extender Business Rule (Once) - Update the value of Load Dashboard Server Task Arguments to the following:
{WSMU}{TestFunction}{}
- The syntax for referencing this object is
{WS}{FunctionName}{Parameter1=Value1}. - The syntax for using the Assembly Service on the Maintenance level is
{WSMU}{FunctionName}{Parameter1=Value1}.
- Click Save.
- Open the newly created Dashboard assembly file. Add the following lines that are highlighted below:
- C#
- Visual Basic
namespace Workspace.__WsNamespacePrefix.__WsAssemblyName
{
public class WsasDashboard : IWsasDashboardV800
{
public XFLoadDashboardTaskResult ProcessLoadDashboardTask(SessionInfo si, BRGlobals brGlobals, DashboardWorkspace workspace, DashboardExtenderArgs args)
{
try
{
if ((brGlobals != null) && (workspace != null) && (args?.LoadDashboardTaskInfo != null))
{
if (args.FunctionName.XFEqualsIgnoreCase("TestFunction"))
{
// Implement Load Dashboard logic here.
if ((args.LoadDashboardTaskInfo.Reason == LoadDashboardReasonType.Initialize) && (args.LoadDashboardTaskInfo.Action == LoadDashboardActionType.BeforeFirstGetParameters))
{
var loadDashboardTaskResult = new XFLoadDashboardTaskResult();
loadDashboardTaskResult.ChangeCustomSubstVarsInDashboard = true;
string value ="You have created a header message using code.";
loadDashboardTaskResult.ModifiedCustomSubstVars.Add("DashboardHeader", $"{value}");
return loadDashboardTaskResult;
}
}
}
return null;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
throw new XFException(si, ex);
}
}
}
}
Namespace Workspace.__WsNamespacePrefix.__WsAssemblyName
Public Class WsasDashboard
Implements IWsasDashboardV800
Public Function ProcessLoadDashboardTask(ByVal si As SessionInfo, ByVal globals As BRGlobals, ByVal workspace As DashboardWorkspace, _
ByVal args As DashboardExtenderArgs) As XFLoadDashboardTaskResult Implements IWsasDashboardV800.ProcessLoadDashboardTask
Try
If (globals IsNot Nothing) AndAlso (workspace IsNot Nothing) AndAlso (args IsNot Nothing) AndAlso (args.LoadDashboardTaskInfo IsNot Nothing) Then
If args.FunctionName.XFEqualsIgnoreCase("TestFunction") Then
'Implement Load Dashboard logic here.
If (args.LoadDashboardTaskInfo.Reason = LoadDashboardReasonType.Initialize) And (args.LoadDashboardTaskInfo.Action = LoadDashboardActionType.BeforeFirstGetParameters) Then
Dim loadDashboardTaskResult As New XFLoadDashboardTaskResult()
loadDashboardTaskResult.ChangeCustomSubstVarsInDashboard = True
Dim value As String = "You have created a header message using code."
loadDashboardTaskResult.ModifiedCustomSubstVars.Add("DashboardHeader", $"{value}")
Return loadDashboardTaskResult
End If
End If
End If
Return Nothing
Catch ex As Exception
Throw New XFException(si, ex)
End Try
End Function
End Class
End Namespace
- Click Save.
- Test the dashboard by clicking View Dashboard. The Dynamic Repeater Dashboard will be displayed in OneStream. Please look at the upper-left hand corner of the dashboard. The message that we wrote in the assembly should be displayed. Below is a screenshot:
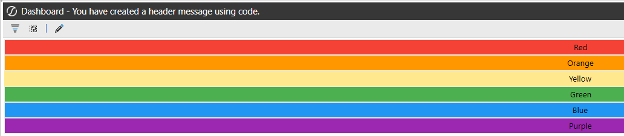
Data Set Service Type
This service type enables you to implement Data Set logic within assemblies. You can either select Data Set Service when adding a new file or choose the Dashboard Data Set business‑rule type. Data Set Services typically execute queries and return their results to data adapters or dashboard parameters via method-based queries.
Service Factory Setup
Start by creating a Service Factory. The Service Factory file is used to interact with dynamic dashboards and allows for the creation of OneStream objects.
- Create a New Workspace
- Name:
Dynamic Dashboard Examples
- Add a Maintenance Unit
- Type:
CodeOnly
- Add an Assembly
- Type:
Code
- Add the Service Factory File
- In the Code section, right‑click Files under
Assembly Filesand choose Add File. - Set Source Code Type to
Service Factory.
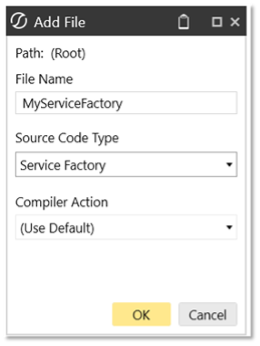
In your MyServiceFactory source code, locate and uncomment the DataSet case statement.
Rename the returning class (Optional)
- C#
- Visual Basic
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Data;
using System.Data.Common;
using System.Globalization;
using System.IO;
using System.Linq;
using Microsoft.CSharp;
using OneStream.Finance.Database;
using OneStream.Finance.Engine;
using OneStream.Shared.Common;
using OneStream.Shared.Database;
using OneStream.Shared.Engine;
using OneStream.Shared.Wcf;
using OneStream.Stage.Database;
using OneStream.Stage.Engine;
using OneStreamWorkspacesApi;
using OneStreamWorkspacesApi.V800;
namespace Workspace.__WsNamespacePrefix.__WsAssemblyName
{
public class MyServiceFactory : IWsAssemblyServiceFactory
{
public IWsAssemblyServiceBase CreateWsAssemblyServiceInstance (SessionInfo si, BRGlobals brGlobals,
DashboardWorkspace workspace, WsAssemblyServiceType wsAssemblyServiceType, string itemName)
{
try
{
switch (wsAssemblyServiceType)
{
//case WsAssemblyServiceType.Component:
// return new WsasComponent();
//case WsAssemblyServiceType.Dashboard:
// return new WsasDashboard();
//case WsAssemblyServiceType.DataManagementStep:
// return new WsasDataManagementStep();
case WsAssemblyServiceType.DataSet:
return new WsasDataSet();
//case WsAssemblyServiceType.DynamicDashboards:
// return new WsasDynamicDashboards();
//case WsAssemblyServiceType.FinanceCore:
// return new WsasFinanceCore();
//case WsAssemblyServiceType.FinanceCustomCalculate:
// return new WsasFinanceCustomCalculate();
//case WsAssemblyServiceType.FinanceGetDataCell:
// return new WsasFinanceGetDataCell();
//case WsAssemblyServiceType.FinanceMemberLists:
// return new WsasFinanceMemberLists();
//case WsAssemblyServiceType.SqlTableEditor:
// return new WsasSqlTableEditor();
//case WsAssemblyServiceType.TableView:
// return new WsasTableView();
//case WsAssemblyServiceType.XFBRString:
// return new WsasXFBRString();
default:
return null;
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
throw new XFException(si, ex);
}
}
}
}
Imports System
Imports System.Collections.Generic
Imports System.Data
Imports System.Data.Common
Imports System.Globalization
Imports System.IO
Imports System.Linq
Imports Microsoft.CSharp
Imports OneStream.Finance.Database
Imports OneStream.Finance.Engine
Imports OneStream.[Shared].Common
Imports OneStream.[Shared].Database
Imports OneStream.[Shared].Engine
Imports OneStream.[Shared].Wcf
Imports OneStream.Stage.Database
Imports OneStream.Stage.Engine
Imports OneStreamWorkspacesApi
Imports OneStreamWorkspacesApi.V800
Namespace Workspace.__WsNamespacePrefix.__WsAssemblyName
Public Class MyServiceFactory
Inherits IWsAssemblyServiceFactory
Public Function CreateWsAssemblyServiceInstance(ByVal si As SessionInfo, ByVal brGlobals As BRGlobals, ByVal workspace As DashboardWorkspace, ByVal wsAssemblyServiceType As WsAssemblyServiceType, ByVal itemName As String) As IWsAssemblyServiceBase
Try
Select Case wsAssemblyServiceType
'Case WsAssemblyServiceType.Component
' Return New WsasComponent()
'Case WsAssemblyServiceType.Dashboard
' Return New WsasDashboard()
'Case WsAssemblyServiceType.DataManagementStep
' Return New WsasDataManagementStep()
Case WsAssemblyServiceType.DataSet
Return New WsasDataSet()
'Case WsAssemblyServiceType.DynamicDashboards
' Return New WsasDynamicDashboards()
'Case WsAssemblyServiceType.FinanceCore
' Return New WsasFinanceCore()
'Case WsAssemblyServiceType.FinanceCustomCalculate
' Return New WsasFinanceCustomCalculate()
'Case WsAssemblyServiceType.FinanceGetDataCell
' Return New WsasFinanceGetDataCell()
'Case WsAssemblyServiceType.FinanceMemberLists
' Return New WsasFinanceMemberLists()
'Case WsAssemblyServiceType.SqlTableEditor
' Return New WsasSqlTableEditor()
'Case WsAssemblyServiceType.TableView
' Return New WsasTableView()
'Case WsAssemblyServiceType.XFBRString
' Return New WsasXFBRString()
Case Else
Return Nothing
End Select
Catch ex As Exception
Throw New XFException(si, ex)
End Try
End Function
End Class
End Namespace
Select the workspace and update the Workspace Assembly Service property value to the format {WsAssemblyName}.{ServiceFactoryName}. For example, set the value to Code.MyServiceFactory.
Data Set Service
Once the Service Factory file has been created and the appropriate lines of code have been uncommented, create a Data Set Service.
- Add a New File:
- Navigate to the Code section.
- In the
Assembly Filespanel, right-click on Files and select Add File. - Set the File Name to match the returning class name.
- Set Source Code Type to
Data Set Service.
Example – Dynamic Dashboard Sample
The following example uses the Dynamic Dashboards sample. The following steps add code to create a data set and add it to our dashboard. For this to function as intended, please ensure the Dynamic Dashboards case statement from the MyServiceFactory code is uncommented.
- Please add the following highlighted code to the newly created Data Set assembly file. This code is like the
GetAnimalNamesmethod in theDTK_HelperQueries.csfile:
- C#
- Visual Basic
public object GetDataSet(SessionInfo si, BRGlobals brGlobals, DashboardWorkspace workspace, DashboardDataSetArgs args)
{
try
{
if ((brGlobals != null) && (workspace != null) && (args != null))
{
if (args.DataSetName.XFEqualsIgnoreCase("MyDataSet"))
{
try
{
List<string> colors = { "Red", "Blue", "Green", "Yellow" };
string tableName = "ColorNames";
DataTable dt = new(tableName);
dt.Columns.Add("Name", Type.GetType("System.String"));
foreach (string color in colors)
{
DataRow dr = dt.NewRow();
dr["Name"] = color;
dt.Rows.Add(dr);
}
using DataView dv = new(dt);
dv.Sort = "Name";
using DataTable dtSorted = dv.ToTable();
dtSorted.TableName = tableName;
return dtSorted;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
throw ErrorHandler.LogWrite(si, new XFException(si, "Unhandled Exception in GetDataSet() function.", ex.Message, ex.InnerException));
}
}
}
return null;
}
}
}
Public Function GetDataSet(ByVal si As SessionInfo, ByVal brGlobals As BRGlobals, ByVal workspace As DashboardWorkspace, ByVal args As DashboardDataSetArgs) As Object
If brGlobals IsNot Nothing AndAlso workspace IsNot Nothing AndAlso args IsNot Nothing Then
If args.DataSetName.XFEqualsIgnoreCase("MyDataSet") Then
Try
Dim colors As New List(Of String) From {"Red", "Blue", "Green", "Yellow"}
Dim tableName As String = "ColorNames"
Dim dt As New DataTable(tableName)
dt.Columns.Add("Name", Type.GetType("System.String"))
For Each color As String In colors
Dim dr As DataRow = dt.NewRow()
dr("Name") = color
dt.Rows.Add(dr)
Next
Dim dtSorted As DataTable
Using dv As New DataView(dt)
dv.Sort = "Name"
dtSorted = dv.ToTable()
End Using
dtSorted.TableName = tableName
Return dtSorted
Catch ex As Exception
Throw ErrorHandler.LogWrite(si, New XFException(si, "Unhandled Exception in GetDataSet() function.", ex.Message, ex.InnerException))
End Try
End If
End If
Return Nothing
End Function
-
Click Save.
-
A parameter to store the data set needs to be created. Under Workspaces -> Dynamic Dashboard Examples -> Maintenance Units -> CodeOnly, click on Parameters, then click on the Create Parameter icon in the toolbar.
-
Configure the parameter as shown in the reference screenshot:
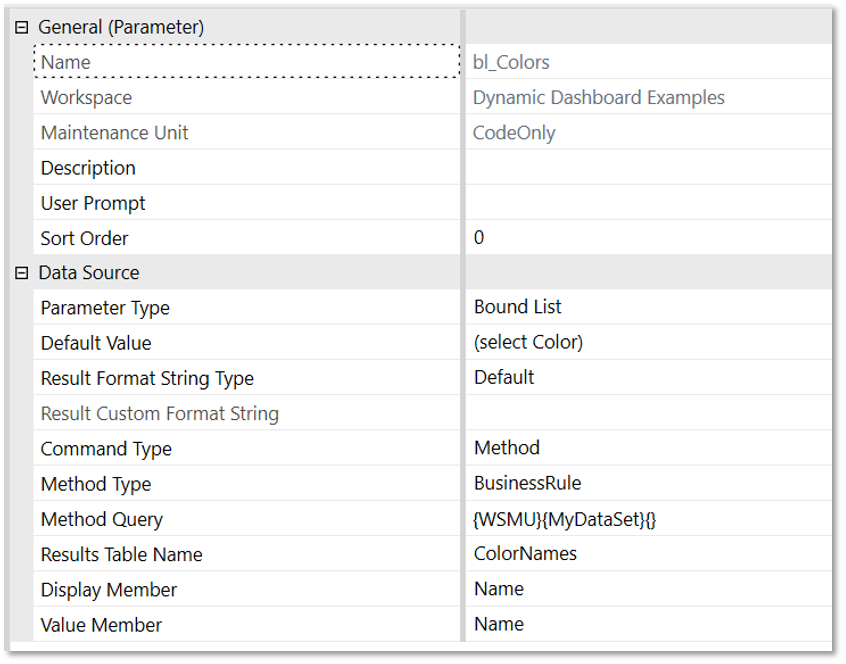
-
A combo box component needs to be created. Under Workspaces -> Dynamic Dashboard Examples -> Maintenance Units -> CodeOnly, click on Components, then click on the Create Dashboard Component icon in the toolbar.
-
Select Combo Box.
-
Below is a screenshot of the component property values when correctly configured. The Display Format value should reflect the following:
- Height =
50 - HorizontalAlignment =
Left - LabelBold =
True - LabelPosition =
Top - LabelTextColor =
XFReadOnlyText - MarginBottom =
5 - MarginLeft =
80 - MarginTop =
10 - VerticalAlignment =
Top - Width =
200
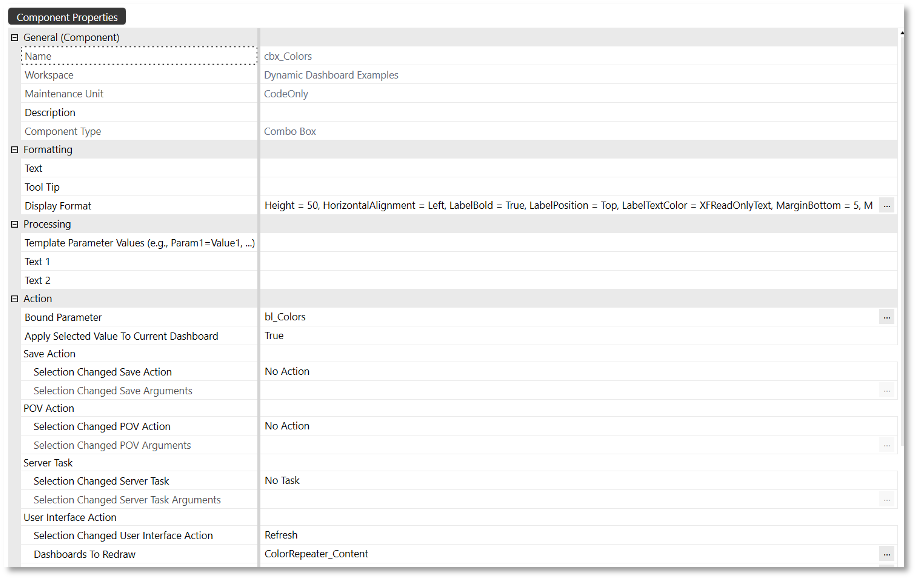
Please note that the Bound Parameter is set to bl_Colors, which is the parameter that was created in step 4.
-
Create a new dashboard to host and display the newly created combo box. Under Workspaces -> Dynamic Dashboard Examples -> Maintenance Units -> CodeOnly -> Dashboard Groups, click on Repeater, then click on the Create Dashboard icon in the toolbar.
-
Under Dashboard Properties, name the dashboard
ComboBox_Dashboard, set the Layout Type toGrid, and set the Number of Rows and Number of Columns to1. The values should reflect the following screenshot:
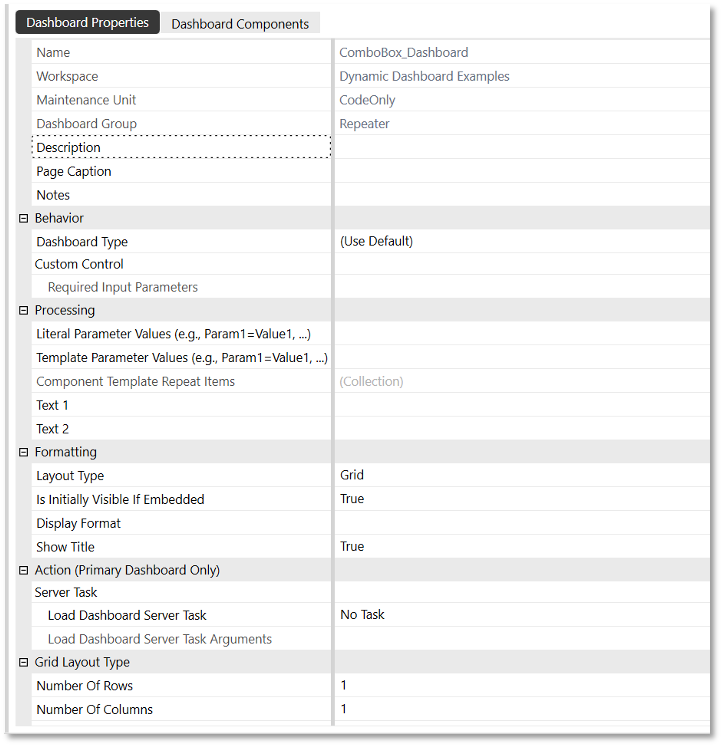
Under Dashboard Components, add the combo box that was created in step 7 to the Dashboard Components list.

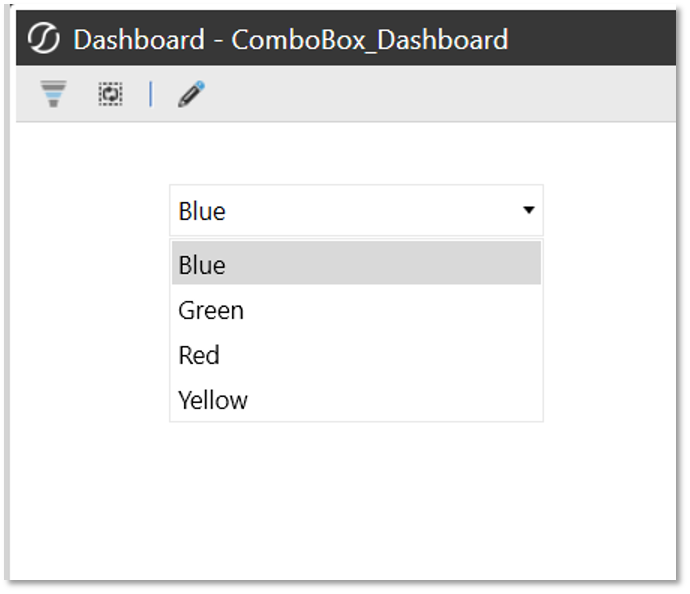
- Click View Dashboard to launch the Combo Box Dashboard in OneStream. The combo box contains all the values that are located in the assembly. A screenshot of the expected output is provided below:
Dynamic Dashboard Service Type
Dynamic dashboards are the most unique of the service types. They allow you to modify components within the dashboard as well as the dashboard itself. Dynamic dashboards enable developers to build and modify dashboards through code. You use workspace assemblies, which enhance the flexibility of your dashboards and reduce time spent within the user interface. This allows you to develop most if not all of your Solution within a Workspace.
Service Factory Setup
Start by creating a Service Factory. The Service Factory file is used to interact with dynamic dashboards and allows for the creation of OneStream objects.
- Create a new Workspace (Minesweeper)
- Add a Maintenance Unit (Minesweeper)
- Add an Assembly (Code) and choose the Compiler Language C# or Visual Basic.
- C#
- Visual Basic
- Click on Code, and under the Assembly Files panel, right-click Files. Then click on Add File. a. Source Code Type = Service Factory
- C#
- Visual Basic
The source code for ServiceFactory.cs is below. Uncomment the DynamicDashboards, Dashboard, and ComponentService case statement for C# or Visual Basic.
Prefix the returning class as Minesweeper_ServiceType();.
namespace Workspace.__WsNamespacePrefix.__WsAssemblyName
{
// The service factory is the entry point for dynamic dashboards
public class ServiceFactory : IWsAssemblyServiceFactory
{
public IWsAssemblyServiceBase CreateWsAssemblyServiceInstance(SessionInfo si, BRGlobals brGlobals,
DashboardWorkspace workspace, WsAssemblyServiceType wsAssemblyServiceType, string itemName)
{
try
{
switch (wsAssemblyServiceType)
{
case WsAssemblyServiceType.DynamicDashboards:
// The dynamic dashboard magic takes place in here
return new Minesweeper_DynamicDashboardsService();
// case WsAssemblyServiceType.XFBRString:
// return new Minesweeper_XFBRService();
//case WsAssemblyServiceType.DataSet:
// return new WsasDataSet();
case WsAssemblyServiceType.Dashboard:
return new Minesweeper_DashboardService();
case WsAssemblyServiceType.Component:
return new Minesweeper_ComponentService();
//case WsAssemblyServiceType.TableView:
// return new WsasTableView();
//case WsAssemblyServiceType.SqlTableEditor:
// return new WsasSqlTableEditor();
default:
return null;
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
throw ErrorHandler.LogWrite(si, new XFException(si, ex));
}
}
}
}
- Select the Maintenance Unit and update the Workspace Assembly Service property to
{WsAssemblyName}.{ServiceFactoryName}. For example,Assembly_Minesweeper.ServiceFactory.
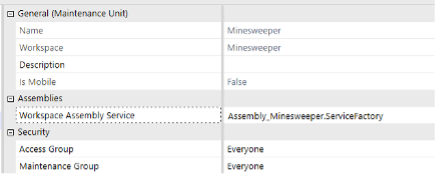
Dynamic Dashboard Service
Once the Service Factory file has been created and the appropriate lines of code have been uncommented, create a Dynamic Dashboard Service. This service is unique, as it enables developers to modify components within the dashboard as well as the dashboard itself.
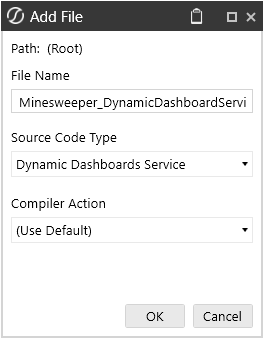
- Click on Code, and under the Assembly Files panel, right-click Files. Then click on Add File.
- File Name = Returning class name
- Source Code Type = Dynamic Dashboards Service
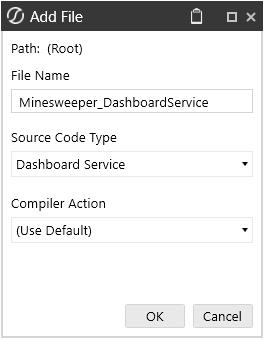
- Click on Code, and under the Assembly Files panel, right-click Files. Then click on Add File.
- File Name = Returning class name
- Source Code Type = Dashboards Service
- Click on Code, and under the Assembly Files panel, right-click Files. Then click on Add File.
- File Name = Returning class name
- Source Code Type = Component Service
Example
An excellent example of dynamic dashboards in action comes from the Minesweeper solution that can be found on the Solution Exchange. Below is a walkthrough:
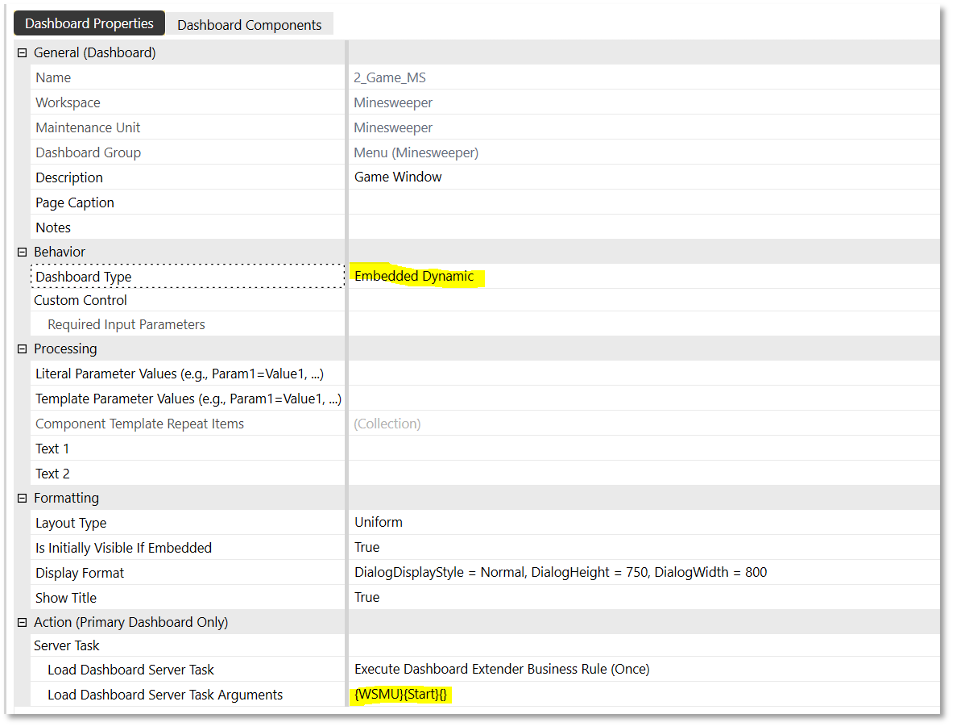
- Once Minesweeper is installed, go to Workspaces > Minesweeper > Maintenance Units > Minesweeper > Dashboard Groups > Menu (Minesweeper) > 2_Game_MS.
- Under Dashboard Properties, you will see that Dashboard Type is set to Embedded Dynamic and Load Dashboard Server Task Arguments is set to
{WSMU}{Start}.
- Go to Workspaces > Minesweeper > Maintenance Units > Minesweeper > Assemblies > Assembly_Minesweeper. Then under Assembly Files, click on
Minesweeper_DashboardsService.cs
The DashboardService assembly sets up the Board objects when loading the dashboard. VB example is not provided.
namespace Workspace.__WsNamespacePrefix.__WsAssemblyName
{
public class Minesweeper_DashboardService : IWsasDashboardV800
{
public XFLoadDashboardTaskResult ProcessLoadDashboardTask(SessionInfo si, BRGlobals brGlobals, DashboardWorkspace workspace, DashboardExtenderArgs args)
{
try
{
if ((brGlobals != null) && (workspace != null) && (args?.LoadDashboardTaskInfo != null))
{
// {WSMU}{Start}{}
if (args.FunctionName.XFEqualsIgnoreCase("Start"))
{
if ((args.LoadDashboardTaskInfo.Reason == LoadDashboardReasonType.Initialize) && (args.LoadDashboardTaskInfo.Action == LoadDashboardActionType.BeforeFirstGetParameters))
{
// Create the board based on the number of rows selected
int rows = BoardGlobals.rows;
int cols = rows;
Board board = new Board(rows, cols);
// static class to share the board
BoardGlobals.board = board;
return new XFLoadDashboardTaskResult();
}
}
}
return null;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
throw ErrorHandler.LogWrite(si, new XFException(si, ex));
}
}
}
}
- Under Assembly Files, click on
Minesweeper_DynamicDashboardsService.cs
This is where the board gets created dynamically. Look over the code to see how everything is getting created.
namespace Workspace.__WsNamespacePrefix.__WsAssemblyName
{
public class Minesweeper_DynamicDashboardsService : IWsasDynamicDashboardsV800
{
public WsDynamicDashboardEx GetEmbeddedDynamicDashboard(SessionInfo si, IWsasDynamicDashboardsApiV800 api, DashboardWorkspace workspace, DashboardMaintUnit maintUnit,
WsDynamicComponentEx parentDynamicComponentEx, Dashboard storedDashboard, Dictionary<string, string> customSubstVarsAlreadyResolved)
{
try
{
if (api != null)
{
// Get the embedded dynamic dashboard from the Dynamic Dashboards API
WsDynamicDashboardEx dynamicDashboardEx = api.GetEmbeddedDynamicDashboard(si, workspace, parentDynamicComponentEx, storedDashboard, string.Empty, null, TriStateBool.Unknown, WsDynamicItemStateType.Unknown);
// Set the layout type to grid
dynamicDashboardEx.DynamicDashboard.LayoutType = DashboardLayoutType.Grid;
// Get number of rows to dynamically set number of rows and columns in the dashboard
int rows = BoardGlobals.rows;
// Dynamically add rows and columns to the dynamic dashboard
var gridRows = new List<XFGridLayoutRowDefinition>();
var gridCols = new List<XFGridLayoutColumnDefinition>();
// The length of the gridRows List sets the number of Rows for the Dynamic Dashboard
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++)
{
// Define each row as Type: Component, Height: *
gridRows.Add(new XFGridLayoutRowDefinition(XFGridLayoutRowColType.Component, "*"));
// Since grid is a square set columns here too
// Define each column as Type: Component, Width: *
gridCols.Add(new XFGridLayoutColumnDefinition(XFGridLayoutRowColType.Component, "*"));
}
// Actually set the grid layout definition
var gridLayoutDefinition = new XFGridLayoutDefinition(gridCols, gridRows);
dynamicDashboardEx.DynamicDashboard.GridLayoutDefinition = gridLayoutDefinition;
int cols = rows;
var repeatArgs = new List<WsDynamicComponentRepeatArgs>();
for (int x = 0; x < rows; x++)
{
for (int y = 0; y < cols; y++)
{
var nextLevelTemplateSubstVarsToAdd = new Dictionary<string, string>
{
// the key in the dictionary is used with ~!key!~ syntax in the dynamic component
// and will be replaced with the value for that key
// ex. With a dictionary equal to {"Hello", "World"}
// ~!Hello!~ becomes World in the component
// ~!CellCoordinates!~ will be replaced with the x and y values of this loop
{ "CellCoordinates", $"{x},{y}" },
{ "CellText", $"{BoardGlobals.board.cells[x,y].GetCellText()}" },
{ "CellDisplayFormat", $"{BoardGlobals.board.cells[x,y].GetCellDisplayFormat()}" }
};
repeatArgs.Add(new WsDynamicComponentRepeatArgs($"{x},{y}", nextLevelTemplateSubstVarsToAdd));
}
}
// Using the tag to pass the repeatArgs around for use later
dynamicDashboardEx.DynamicDashboard.Tag = repeatArgs;
api.SaveDynamicDashboardState(si, parentDynamicComponentEx.DynamicComponent, dynamicDashboardEx, WsDynamicItemStateType.EntireObject);
return dynamicDashboardEx;
}
return null;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
throw ErrorHandler.LogWrite(si, new XFException(si, ex));
}
}
public WsDynamicComponentCollection GetDynamicComponentsForDynamicDashboard(SessionInfo si, IWsasDynamicDashboardsApiV800 api, DashboardWorkspace workspace,
DashboardMaintUnit maintUnit, WsDynamicDashboardEx dynamicDashboardEx, Dictionary<string, string> customSubstVarsAlreadyResolved)
{
try
{
if (api != null)
{
var repeatArgsList = dynamicDashboardEx.DynamicDashboard.Tag as List<WsDynamicComponentRepeatArgs>;
// this part is magic
// the length of this list seems to determine the number of components to create dynamically
// this list is also used for substituting the ~!key!~ with the values set earlier
var componentCollection = api.GetDynamicComponentsRepeatedForDynamicDashboard(si, workspace, dynamicDashboardEx, repeatArgsList, TriStateBool.Unknown, WsDynamicItemStateType.Unknown);
return componentCollection;
}
return null;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
throw ErrorHandler.LogWrite(si, new XFException(si, ex));
}
}
// Ignore. have to keep this here to fulfill the interface contract
public WsDynamicAdapterCollection GetDynamicAdaptersForDynamicComponent(SessionInfo si, IWsasDynamicDashboardsApiV800 api, DashboardWorkspace workspace,
DashboardMaintUnit maintUnit, WsDynamicComponentEx dynamicComponentEx, Dictionary<string, string> customSubstVarsAlreadyResolved)
{
try
{
if (api != null)
{
return api.GetDynamicAdaptersForDynamicComponent(si, workspace, dynamicComponentEx, string.Empty, null, TriStateBool.Unknown, WsDynamicItemStateType.Unknown);
}
return null;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
throw ErrorHandler.LogWrite(si, new XFException(si, ex));
}
}
// Ignore. have to keep this here to fulfill the interface contract
public WsDynamicCubeViewEx GetDynamicCubeViewForDynamicAdapter(SessionInfo si, IWsasDynamicDashboardsApiV800 api, DashboardWorkspace workspace,
DashboardMaintUnit maintUnit, WsDynamicAdapterEx dynamicAdapterEx, CubeViewItem storedCubeViewItem, Dictionary<string, string> customSubstVarsAlreadyResolved)
{
try
{
if (api != null)
{
return api.GetDynamicCubeViewForDynamicAdapter(si, workspace, dynamicAdapterEx, storedCubeViewItem, string.Empty, null, TriStateBool.Unknown, WsDynamicItemStateType.Unknown);
}
return null;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
throw ErrorHandler.LogWrite(si, new XFException(si, ex));
}
}
}
}
namespace Workspace.__WsNamespacePrefix.__WsAssemblyName
{
public class Minesweeper_ComponentService : IWsasComponentV800
{
public XFSelectionChangedTaskResult ProcessComponentSelectionChanged(SessionInfo si, BRGlobals brGlobals, DashboardWorkspace workspace, DashboardExtenderArgs args)
{
try
{
// {WSMU}{CellClicked}{cell=[~!CellCoordinates!~]}
// Called when clicking a cell
if (args.FunctionName.XFEqualsIgnoreCase("CellClicked") && !BoardGlobals.isGameOver)
{
return CheckClickedCell(si, args);
}
// {WSMU}{SetBoardGlobals}{RowsAndColumns=|!RowsAndColumns_MS!|,BombPercentage=|!BombPercentage_MS!|}
// RowsAndColumns_MS is a bound parameter set by a combo box component
// BombPercentage_MS is a bound parameter set by a combo box component
else if (args.FunctionName.XFEqualsIgnoreCase("BombButtonClicked"))
{
ButtonMethod(si, args, "BombDisplay", "FlagDisplay");
}
else if (args.FunctionName.XFEqualsIgnoreCase("FlagButtonClicked"))
{
ButtonMethod(si, args, "FlagDisplay", "BombDisplay");
}
else if (args.FunctionName.XFEqualsIgnoreCase("SetBoardGlobals"))
{
int rows;
int.TryParse(args.NameValuePairs.XFGetValue("RowsAndColumns", string.Empty), out rows);
int bombPercentage;
int.TryParse(args.NameValuePairs.XFGetValue("BombPercentage", string.Empty), out bombPercentage);
BoardGlobals.rows = rows;
BoardGlobals.cols = rows;
BoardGlobals.bombPercentage = (bombPercentage / 100f);
int totalBombCells = (int) (BoardGlobals.rows * BoardGlobals.cols * BoardGlobals.bombPercentage);
BRApi.Dashboards.Parameters.SetLiteralParameterValue(si, false, args.PrimaryDashboard.WorkspaceID, "NumberOfFlags", totalBombCells.ToString());
BRApi.Dashboards.Parameters.SetLiteralParameterValue(si, false, args.PrimaryDashboard.WorkspaceID, "BombOrFlagOption", "Flag");
BoardGlobals.isGameOver = false;
}
// {WSMU}{Uninstall}{}
else if (args.FunctionName.XFEqualsIgnoreCase("Uninstall"))
{
return UninstallSolution(si, args);
}
return null;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
throw ErrorHandler.LogWrite(si, new XFException(si, ex));
}
}
private XFSelectionChangedTaskResult CheckClickedCell(SessionInfo si, DashboardExtenderArgs args)
{
var selectionChangedTaskResult = new XFSelectionChangedTaskResult();
bool showMessage = false;
string message = string.Empty;
// Get the cell coordinates, passed as a parameter on the cell's button
string cell = args.NameValuePairs.XFGetValue("cell");
int[] cellCoords = Array.ConvertAll(cell.Split(','), s => int.Parse(s));
int x = cellCoords[0];
int y = cellCoords[1];
// Call the logic for when that particular cell is clicked based on it's coordinates
BoardGlobals.board.ClickCell(x, y, si, args);
// Check if the player has lost
if (BoardGlobals.board.cells[x, y].isRevealed && BoardGlobals.board.cells[x, y].isBomb)
{
showMessage = true;
message = "YOU LOSE";
BoardGlobals.board.RevealAllUnflaggedCells();
BoardGlobals.isGameOver = true;
}
// Otherwise, check if the player has won
else if (BoardGlobals.board.CheckWin())
{
showMessage = true;
message = "YOU WIN";
BoardGlobals.isGameOver = true;
}
selectionChangedTaskResult.IsOK = true;
selectionChangedTaskResult.ShowMessageBox = showMessage;
selectionChangedTaskResult.Message = message;
return selectionChangedTaskResult;
}
private XFSelectionChangedTaskResult UninstallSolution(SessionInfo si, DashboardExtenderArgs args)
{
StringBuilder message = new StringBuilder();
var taskResult = new XFSelectionChangedTaskResult();
try
{
if (BRApi.Security.Authorization.IsUserInAdminGroup(si))
{
// Remove workspace
BRApi.Dashboards.Workspaces.DeleteWorkspace(si, false, args.PrimaryDashboard.WorkspaceID, true);
// Remove dashboard profiles
DropDashboardProfiles(si);
message.AppendLine($"{m_SolutionName} Uninstalled");
message.AppendLine("To Complete the Process:");
message.AppendLine("1) Close the Dialog");
message.AppendLine("2) Close the Dashboard Page");
BRApi.ErrorLog.LogMessage(si, $"{m_SolutionName} Uninstalled");
taskResult.IsOK = true;
taskResult.ShowMessageBox = true;
taskResult.Message = message.ToString();
}
else
{
message.AppendLine("Security Error: Administration Rights Required to Execute Uninstall");
}
return taskResult;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
throw ErrorHandler.LogWrite(si, new XFException(si, ex));
}
}
private void DropDashboardProfiles(SessionInfo si)
{
try
{
string message = string.Empty;
string[] dashboardProfiles = { m_MinesweeperDashboardProfileName };
var dashboardWcf = new Dashboards();
foreach (string profile in dashboardProfiles)
{
var dashboardProfile = dashboardWcf.GetProfileUsingName(si, false, profile, true);
if (dashboardProfile != null)
{
dashboardWcf.DeleteProfile(si, false, dashboardProfile.Profile.UniqueID);
}
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
throw ErrorHandler.LogWrite(si, new XFException(si, ex));
}
}
private static XFSelectionChangedTaskResult SetReturnObject(SessionInfo si)
{
try
{
XFSelectionChangedTaskResult taskResult = new()
{
ChangeCustomSubstVarsInDashboard = true,
ChangeSelectionChangedUIActionInDashboard = true
};
return taskResult;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
throw ErrorHandler.LogWrite(si, new XFException(si, ex));
}
}
private void ButtonMethod(SessionInfo si,DashboardExtenderArgs args, string button1, string button2)
{
string button1Display = ButtonDisplay("XFWorkflowInProcess", "Black", "True", "Black");
string button2Display = ButtonDisplay("White", "Gray", "False", "White");
BRApi.Dashboards.Parameters.SetLiteralParameterValue(si, false, args.PrimaryDashboard.WorkspaceID, button1, button1Display);
BRApi.Dashboards.Parameters.SetLiteralParameterValue(si, false, args.PrimaryDashboard.WorkspaceID, button2, button2Display);
}
private string ButtonDisplay(string backgroundColor, string textColor, string isBold, string borderColor)
{
return $"BackgroundColor = {backgroundColor}, TextColor = {textColor}, Bold = {isBold}, HoverColor = XFWorkflowInProcess, BorderColor = {borderColor}";
}
#region Constants
private const string m_SolutionName = "Minesweeper";
private const string m_MinesweeperDashboardProfileName = "Minesweeper";
#endregion
}
}
namespace Workspace.__WsNamespacePrefix.__WsAssemblyName
{
public class Minesweeper_DynamicDashboardsService : IWsasDynamicDashboardsV800
{
public WsDynamicDashboardEx GetEmbeddedDynamicDashboard(SessionInfo si, IWsasDynamicDashboardsApiV800 api, DashboardWorkspace workspace, DashboardMaintUnit maintUnit,
WsDynamicComponentEx parentDynamicComponentEx, Dashboard storedDashboard, Dictionary<string, string> customSubstVarsAlreadyResolved)
{
try
{
if (api != null)
{
// Get the embedded dynamic dashboard from the Dynamic Dashboards API
WsDynamicDashboardEx dynamicDashboardEx = api.GetEmbeddedDynamicDashboard(si, workspace, parentDynamicComponentEx, storedDashboard, string.Empty, null, TriStateBool.Unknown, WsDynamicItemStateType.Unknown);
// Set the layout type to grid
dynamicDashboardEx.DynamicDashboard.LayoutType = DashboardLayoutType.Grid;
// Get number of rows to dynamically set number of rows and columns in the dashboard
int rows = BoardGlobals.rows;
// Dynamically add rows and columns to the dynamic dashboard
var gridRows = new List<XFGridLayoutRowDefinition>();
var gridCols = new List<XFGridLayoutColumnDefinition>();
// The length of the gridRows List sets the number of Rows for the Dynamic Dashboard
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++)
{
// Define each row as Type: Component, Height: *
gridRows.Add(new XFGridLayoutRowDefinition(XFGridLayoutRowColType.Component, "*"));
// Since grid is a square set columns here too
// Define each column as Type: Component, Width: *
gridCols.Add(new XFGridLayoutColumnDefinition(XFGridLayoutRowColType.Component, "*"));
}
// Actually set the grid layout definition
var gridLayoutDefinition = new XFGridLayoutDefinition(gridCols, gridRows);
dynamicDashboardEx.DynamicDashboard.GridLayoutDefinition = gridLayoutDefinition;
int cols = rows;
var repeatArgs = new List<WsDynamicComponentRepeatArgs>();
for (int x = 0; x < rows; x++)
{
for (int y = 0; y < cols; y++)
{
var nextLevelTemplateSubstVarsToAdd = new Dictionary<string, string>
{
// the key in the dictionary is used with ~!key!~ syntax in the dynamic component
// and will be replaced with the value for that key
// ex. With a dictionary equal to {"Hello", "World"}
// ~!Hello!~ becomes World in the component
// ~!CellCoordinates!~ will be replaced with the x and y values of this loop
{ "CellCoordinates", $"{x},{y}" },
{ "CellText", $"{BoardGlobals.board.cells[x,y].GetCellText()}" },
{ "CellDisplayFormat", $"{BoardGlobals.board.cells[x,y].GetCellDisplayFormat()}" }
};
repeatArgs.Add(new WsDynamicComponentRepeatArgs($"{x},{y}", nextLevelTemplateSubstVarsToAdd));
}
}
// Using the tag to pass the repeatArgs around for use later
dynamicDashboardEx.DynamicDashboard.Tag = repeatArgs;
api.SaveDynamicDashboardState(si, parentDynamicComponentEx.DynamicComponent, dynamicDashboardEx, WsDynamicItemStateType.EntireObject);
return dynamicDashboardEx;
}
return null;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
throw ErrorHandler.LogWrite(si, new XFException(si, ex));
}
}
public WsDynamicComponentCollection GetDynamicComponentsForDynamicDashboard(SessionInfo si, IWsasDynamicDashboardsApiV800 api, DashboardWorkspace workspace,
DashboardMaintUnit maintUnit, WsDynamicDashboardEx dynamicDashboardEx, Dictionary<string, string> customSubstVarsAlreadyResolved)
{
try
{
if (api != null)
{
var repeatArgsList = dynamicDashboardEx.DynamicDashboard.Tag as List<WsDynamicComponentRepeatArgs>;
// this part is magic
// the length of this list seems to determine the number of components to create dynamically
// this list is also used for substituting the ~!key!~ with the values set earlier
var componentCollection = api.GetDynamicComponentsRepeatedForDynamicDashboard(si, workspace, dynamicDashboardEx, repeatArgsList, TriStateBool.Unknown, WsDynamicItemStateType.Unknown);
return componentCollection;
}
return null;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
throw ErrorHandler.LogWrite(si, new XFException(si, ex));
}
}
// Ignore. have to keep this here to fulfill the interface contract
public WsDynamicAdapterCollection GetDynamicAdaptersForDynamicComponent(SessionInfo si, IWsasDynamicDashboardsApiV800 api, DashboardWorkspace workspace,
DashboardMaintUnit maintUnit, WsDynamicComponentEx dynamicComponentEx, Dictionary<string, string> customSubstVarsAlreadyResolved)
{
try
{
if (api != null)
{
return api.GetDynamicAdaptersForDynamicComponent(si, workspace, dynamicComponentEx, string.Empty, null, TriStateBool.Unknown, WsDynamicItemStateType.Unknown);
}
return null;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
throw ErrorHandler.LogWrite(si, new XFException(si, ex));
}
}
// Ignore. have to keep this here to fulfill the interface contract
public WsDynamicCubeViewEx GetDynamicCubeViewForDynamicAdapter(SessionInfo si, IWsasDynamicDashboardsApiV800 api, DashboardWorkspace workspace,
DashboardMaintUnit maintUnit, WsDynamicAdapterEx dynamicAdapterEx, CubeViewItem storedCubeViewItem, Dictionary<string, string> customSubstVarsAlreadyResolved)
{
try
{
if (api != null)
{
return api.GetDynamicCubeViewForDynamicAdapter(si, workspace, dynamicAdapterEx, storedCubeViewItem, string.Empty, null, TriStateBool.Unknown, WsDynamicItemStateType.Unknown);
}
return null;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
throw ErrorHandler.LogWrite(si, new XFException(si, ex));
}
}
}
}
SQL Table Editor Service Type
The SQL Table Editor service type enables you to create a SqlTableEditorSaveData function within a Dashboard Extender rule (assemblies). You can select this service type directly or choose the “Dashboard Extender” business rule type. These rules are typically used for custom actions in Workspaces—such as saving data from the SQL Table Editor component.
Service Factory Setup
Start by creating a Service Factory. The Service Factory file is used to interact with dynamic dashboards and allows for the creation of OneStream objects.
- Create a new Workspace (Dynamic Dashboard Examples)
- Add a Maintenance Unit (CodeOnly)
- Add an Assembly (Code)
- Create a new folder named ‘Factory’ and add a new file
-
File Name =
MyServiceFactory -
Source Code Type =
Service Factory
- Uncomment the
SQLTableEditorcase statement
- Rename the returning class (optional)
- C#
- VB.NET
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Data;
using System.Data.Common;
using System.Globalization;
using System.IO;
using System.Linq;
using Microsoft.CSharp;
using OneStream.Finance.Database;
using OneStream.Finance.Engine;
using OneStream.Shared.Common;
using OneStream.Shared.Database;
using OneStream.Shared.Engine;
using OneStream.Shared.Wcf;
using OneStream.Stage.Database;
using OneStream.Stage.Engine;
using OneStreamWorkspacesApi;
using OneStreamWorkspacesApi.V800;
namespace Workspace.__WsNamespacePrefix.__WsAssemblyName
{
public class MyServiceFactory : IWsAssemblyServiceFactory
{
public IWsAssemblyServiceBase CreateWsAssemblyServiceInstance(SessionInfo si, BRGlobals brGlobals, DashboardWorkspace workspace, WsAssemblyServiceType wsAssemblyServiceType, string itemName)
{
try
{
switch (wsAssemblyServiceType)
{
// case WsAssemblyServiceType.DynamicDashboards:
// return new WsasDynamicDashboards();
// case WsAssemblyServiceType.XFBRString:
// return new WsasXFBRString();
// case WsAssemblyServiceType.DataSet:
// return new WsasDataSet();
// case WsAssemblyServiceType.Dashboard:
// return new WsasDashboard();
// case WsAssemblyServiceType.Component:
// return new WsasComponent();
// case WsAssemblyServiceType.TableView:
// return new WsasTableView();
case WsAssemblyServiceType.SqlTableEditor:
return new WsasSqlTableEditor();
// case WsAssemblyServiceType.DataManagementStep:
// return new WsasDataManagementStep();
default:
return null;
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
throw ErrorHandler.LogWrite(si, new XFException(si, ex));
}
}
}
}
Imports System
Imports System.Collections.Generic
Imports System.Data
Imports System.Data.Common
Imports System.Globalization
Imports System.IO
Imports System.Linq
Imports Microsoft.CSharp
Imports OneStream.Finance.Database
Imports OneStream.Finance.Engine
Imports OneStream.[Shared].Common
Imports OneStream.[Shared].Database
Imports OneStream.[Shared].Engine
Imports OneStream.[Shared].Wcf
Imports OneStream.Stage.Database
Imports OneStream.Stage.Engine
Imports OneStreamWorkspacesApi
Imports OneStreamWorkspacesApi.V800
Namespace Workspace.__WsNamespacePrefix.__WsAssemblyName
Public Class MyServiceFactory
Inherits IWsAssemblyServiceFactory
Public Function CreateWsAssemblyServiceInstance(ByVal si As SessionInfo, ByVal brGlobals As BRGlobals, ByVal workspace As DashboardWorkspace, ByVal wsAssemblyServiceType As WsAssemblyServiceType, ByVal itemName As String) As IWsAssemblyServiceBase
Try
Select Case wsAssemblyServiceType
' Case WsAssemblyServiceType.DynamicDashboards
' Return New WsasDynamicDashboards()
' Case WsAssemblyServiceType.XFBRString
' Return New WsasXFBRString()
' Case WsAssemblyServiceType.DataSet
' Return New WsasDataSet()
' Case WsAssemblyServiceType.Dashboard
' Return New WsasDashboard()
' Case WsAssemblyServiceType.Component
' Return New WsasComponent()
' Case WsAssemblyServiceType.TableView
' Return New WsasTableView()
Case WsAssemblyServiceType.SqlTableEditor
Return New WsasSqlTableEditor()
' Case WsAssemblyServiceType.DataManagementStep
' Return New WsasDataManagementStep()
Case Else
Return Nothing
End Select
Catch ex As Exception
Throw ErrorHandler.LogWrite(si, New XFException(si, ex))
End Try
End Function
End Class
End Namespace
- Select the workspace and set the Workspace Assembly Service property using the format
{WsAssemblyName}.{ServiceFactoryName}. For example,Code.MyServiceFactory.
SQL Table Editor Service
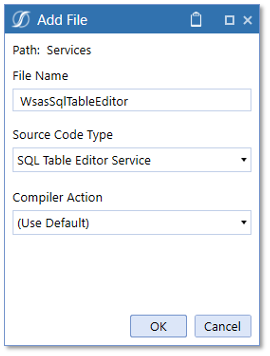
After creating the Service Factory and uncommenting the necessary code, proceed to create the SQL Table Editor Service:
- Create a new folder named ‘Services’ and add a new file.
- File Name = Returning function name from Service Factory file
- Source Code Type = SQL Table Editor Service
Example
To invoke the SQL Table Editor service, use the following reference syntax:
{WS}{FunctionName}{Parameter1=Value1}
This format is the same as what you would use for Dashboard and Component service types.
Table View Service Type
The Table View service type enables you to create a SqlTableEditorSaveData function within a Dashboard Extender rule (assemblies). You can select this service type directly or use the “Spreadsheet” business rule type. These rules are designed to query and update data that resides outside of a cube—either in a spreadsheet or via the Excel Add-In—providing flexibility for non-cube data scenarios.
Service Factory Setup
Start by creating a Service Factory. The Service Factory file is used to interact with dynamic dashboards and allows for the creation of OneStream objects.
-
Create a new Workspace (Dynamic Dashboard Examples)
-
Add a Maintenance Unit (CodeOnly)
-
Add an Assembly (Code)
-
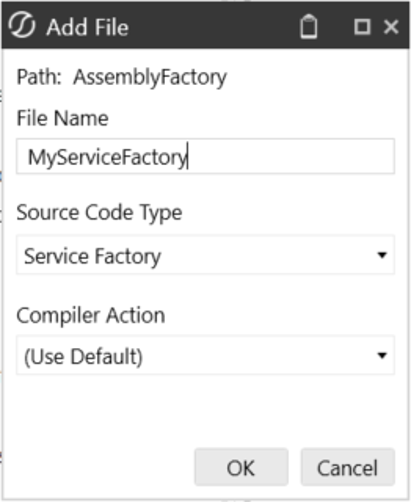
Create a new folder named ‘Factory’ or ‘AssemblyFactory’
-
Add a new file (
MyServiceFactory) -
Source Code Type = Service Factory
- Uncomment the
TableViewcase statement
- Rename the returning class (optional)
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Data;
using System.Data.Common;
using System.Globalization;
using System.IO;
using System.Linq;
using Microsoft.CSharp;
using OneStream.Finance.Database;
using OneStream.Finance.Engine;
using OneStream.Shared.Common;
using OneStream.Shared.Database;
using OneStream.Shared.Engine;
using OneStream.Shared.Wcf;
using OneStream.Stage.Database;
using OneStream.Stage.Engine;
using OneStreamWorkspacesApi;
using OneStreamWorkspacesApi.V800;
namespace Workspace.__WsNamespacePrefix.__WsAssemblyName
{
public class wsServiceFactory : IWsAssemblyServiceFactory
{
public IWsAssemblyServiceBase CreateWsAssemblyServiceInstance(SessionInfo si, BRGlobals brGlobals,
DashboardWorkspace workspace, WsAssemblyServiceType wsAssemblyServiceType, string itemName)
{
try
{
switch (wsAssemblyServiceType)
{
//case WsAssemblyServiceType.Component:
// return new WsasComponent();
//case WsAssemblyServiceType.Dashboard:
// return new WsasDashboard();
//case WsAssemblyServiceType.DataManagementStep:
// return new WsasDataManagementStep();
//case WsAssemblyServiceType.DataSet:
// return new WsasDataSet();
//case WsAssemblyServiceType.DynamicDashboards:
// return new WsasDynamicDashboards();
//case WsAssemblyServiceType.FinanceCore:
// return new WsasFinanceCore();
//case WsAssemblyServiceType.FinanceCustomCalculate:
// return new WsasFinanceCustomCalculate();
//case WsAssemblyServiceType.FinanceGetDataCell:
// return new WsasFinanceGetDataCell();
//case WsAssemblyServiceType.FinanceMemberLists:
// return new WsasFinanceMemberLists();
//case WsAssemblyServiceType.SqlTableEditor:
// return new WsasSqlTableEditor();
case WsAssemblyServiceType.TableView:
return new WsasTableView();
//case WsAssemblyServiceType.XFBRString:
// return new WsasXFBRString();
default:
return null;
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
throw new XFException(si, ex);
}
}
}
}
- Select the workspace and set the Workspace Assembly Service property using the format
{WsAssemblyName}.{ServiceFactoryName}. For example,Code.MyServiceFactory.

Table View Service
After creating the Service Factory and uncommenting the necessary code, proceed to create the Table View Service:
- Create a new folder named ‘Services’ and add a new file.
- File Name = Returning function name from Service Factory file
- Source Code Type = Table View Service
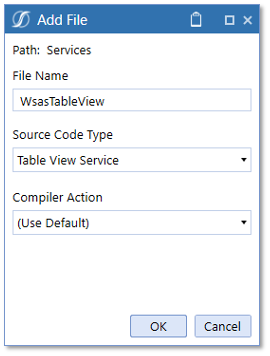
Example
To invoke the Table View service, use the following reference syntax: Workspace.WorkspaceName.AssemblyName.FileName
XFBRString Service Type
This service type lets you create an XFBR String within assemblies. You can do this by choosing this service type or by choosing the Dashboard String Function business rule. These rules are generally used to create effects similar to parameters and substitution variables but allow greater flexibility by using code to return string values in dashboards, cube views, and extensible documents.
Service Factory Setup
Start by creating a Service Factory. The Service Factory file is used to interact with dynamic dashboards and allows for the creation of OneStream objects.
-
Create a new Workspace (Dynamic Dashboard Examples)
-
Add a Maintenance Unit (CodeOnly)
-
Add an Assembly (Code)
-
Create a new folder named ‘Factory’ or ‘AssemblyFactory’
-
Add a new file (
MyServiceFactory) -
Source Code Type = Service Factory
- Uncomment the XFBRString case statement
- Rename the returning class (optional)
public class MUAssemblyFactoryDebug : IWsAssemblyServiceFactory
#else
namespace Workspace.__WsNamespacePrefix.__WsAssemblyName
{
public class MyServiceFactory : IWsAssemblyServiceFactory
#endif
{
public IWsAssemblyServiceBase CreateWsAssemblyServiceInstance(SessionInfo si, BRGlobals brGlobals,
DashboardWorkspace workspace, WsAssemblyServiceType wsAssemblyServiceType, string itemName)
{
try
{
switch (wsAssemblyServiceType)
{
case WsAssemblyServiceType.DynamicDashboards:
return new SvcDynamicDashboards();
case WsAssemblyServiceType.XFBRString:
return new SvcXFBRString();
case WsAssemblyServiceType.DataSet:
return new SvcDataSet();
case WsAssemblyServiceType.Dashboard:
return new SvcDashboard();
case WsAssemblyServiceType.Component:
return new SvcComponent();
case WsAssemblyServiceType.TableView:
return new SvcTableView();
case WsAssemblyServiceType.SqlTableEditor:
return new SvcSqlTableEditor();
case WsAssemblyServiceType.DataManagementStep:
return new SvcDataManagementStep();
default:
return null;
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
throw ErrorHandler.LogWrite(si, new XFException(si, ex));
}
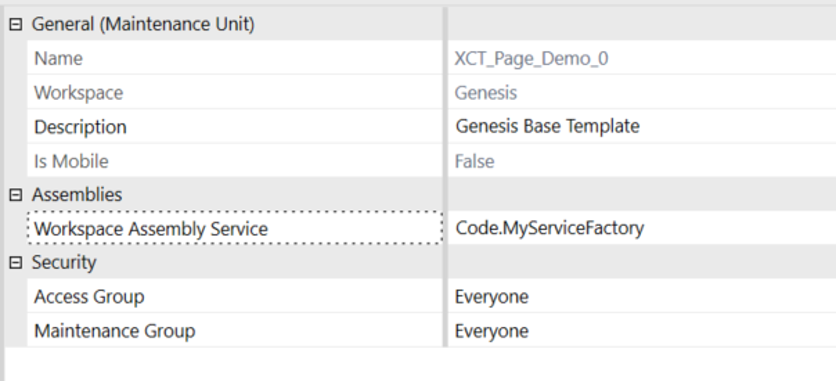
- Select the workspace and update the Workspace Assembly Service property to
{WsAssemblyName}.{ServiceFactoryName}. For example,Code.MyServiceFactory
XFBRString Service
Once the Service Factory file has been created and the appropriate lines of code have been uncommented, create a XFBRString Service.
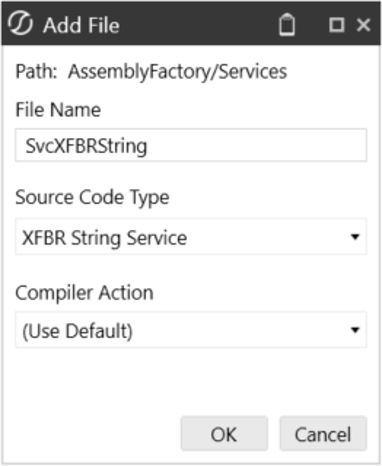
- Create a new folder named ‘Services’ and add a new file
- File Name = Returning function name from Service Factory file. For example
SvcXFBRString. - Source Code Type = XFBR String Service
After that add a method and the code to return a string.
if (args.FunctionName.XFEqualsIgnoreCase("GetPageCaption"))
{
code....
return string
}
Example
In this example, we will create a method in the XFBRString service assembly file that returns a page caption in a dashboard. This is commonly used to query an object or to create a dynamic page caption.
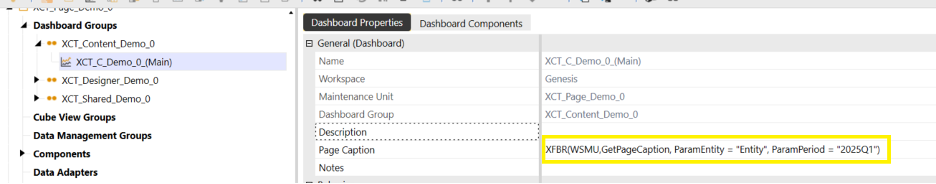
-
In the dashboard, add the method name for the Page Caption.
-
The syntax for calling this method in the current assembly is:
XFBR(WS.MethodName, ParameterName = parametervalue) -
The syntax for calling this method on the Maintenance Units level is:
XFBR(WSMU.MethodName, ParameterName = parametervalue)
- For example:
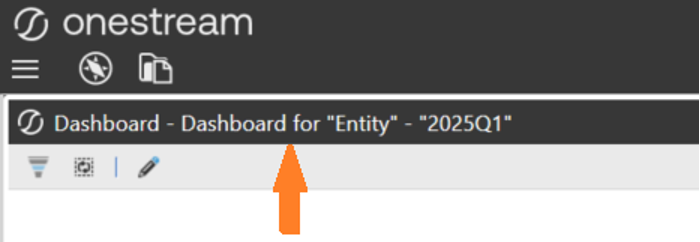
XFBR(WSMU,GetPageCaption, ParamEntity = "Entity", ParamPeriod = "2025Q1")
- In the SvcXFBRString service add this code:
namespace Workspace.__WsNamespacePrefix.__WsAssemblyName
{
public class SvcXFBRString : IWsasXFBRStringV800
{
public string GetXFBRString(SessionInfo si, BRGlobals brGlobals, DashboardWorkspace workspace, DashboardStringFunctionArgs args)
{
try
{
if ((brGlobals != null) && (workspace != null) && (args != null))
{
// Content XFBR Method Calls
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
if (args.FunctionName.XFEqualsIgnoreCase("GetPageCaption"))
{
string paramEntity = args.NameValuePairs["ParamEntity"];
string paramPeriod = args.NameValuePairs["ParamPeriod"];
return $"Dashboard for {paramEntity} - {paramPeriod}";
}
}
return null;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
throw ErrorHandler.LogWrite(si, new XFException(si, ex));
}
}
}
}
This method will take two parameters and it will return a string that will be shown in the Dashboard Page Caption area.